- Industry
- Region
- Country / Region
On May 21, 2024, the European Commission published Directive (EU) 2024/1416 in the Official Journal of the European Commission, updating the exemption clause on cadmium in Annex III of the RoHS Directive (2011/65/EU), extending the exemption period of Article 39(a) and adding an exemption of Article 39(b). The directive will enter into force 20 days after its issuance and will come into force on January 1, 2025.
The specific updates are as follows:
| Item | the scope and duration of | the exemption |
|---|---|---|
| 39(a) | for the downshifting of cadmium-based semiconductor nanocrystalline quantum dots in display lighting applications (less than 0.2 μg of cadmium per square millimeter of light-emitting region). | Applies to all types, with an exemption deadline of 21 November 2025 |
| 39(b) | Cadmium (less than 5 μg per square millimeter on the surface of an LED chip) in downshifting semiconductor nanocrystalline quantum dots deposited directly on LED semiconductor chips for display and projection applications, with a maximum of 1 mg per device | Applies to all types, with an exemption deadline of 31 December 2027 |
Click on this link to view the original Directive (EU) 2024/1416.
On 7 May 2024, the European Commission published a Notice of Guidance for the Interpretation of the Common Charger Directive in the Official Journal of the European Union to assist in the interpretation and implementation of Directive (EU) 2022/2380. In the form of a Q&A, the guide answers some of the most frequently asked questions about the Common Charger Directive with a total of 51 questions, such as whether it only applies to rechargeable devices; whether products that only support wireless charging can be exempted; whether products that only support DC charging (without AC/DC adapters) can be exempted; whether products with a maximum power of more than 240W can be exempted; whether the regulations cover USB cables, etc.
Click on this link to view the original Common Charger Directive Interpretation Guide.
The European Commission launched a public consultation on the operation of Regulation (EU) 1025/2012 on 2 May 2024. They are important for identifying deficiencies in existing legislation and for developing the European standardization system in the future. Consulting stakeholders will provide valuable information for the assessment.
Click this link to check the original public consultation, and the consultation is open until 25 July 2024.
On April 24, 2024, the European Commission launched a study exploring the possibility of digitizing and collecting the conformity assessment certificates of all CE-marked products into a database called the "Digital Solution for Conformity Verification" (DSCV). The objective of the DSCV is to facilitate market surveillance and customs control and to provide more accessible and reliable data on the CE marking of products. Relevant stakeholders, such as customs authorities, market surveillance bodies, certification bodies, notified bodies, manufacturers, distributors, importers, exporters, consumers, and managers of existing similar databases, were invited to participate in the study.
Click on the this link to view the original questionnaire, which was collected until May 17, 2024.
On January 31, 2024, the EU cybersecurity certification scheme on Common Criteria (EUCC), drafted by the European Cybersecurity Agency (ENISA), has been adopted by the European Commission as the first certification scheme within the EU Cybersecurity Certification Framework. The certification program will apply to all ICT products. While the implementation of the certification scheme is part of EU law, this cybersecurity certification framework is voluntary. The EUCC will eventually replace the previous national certification scheme established under the SOG-IS protocol. The certification program has been approved and will be published in the Official Journal (OJ) one year after the date of publication.
Click this link to view ENISA's press release regarding EUCC, click this link to view the original EUCC regulation.
On 1 December 2023, the European Commission published Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2023/2669 amending the implementing decision (EU) 2022/2191 on harmonised standards for wireless communication devices used at or near the human body.
The harmonized standards EN 50360:2017/A1:2023 and EN 50566:2017/A1:2023 are used to cover the essential requirements set out in Article 3 of the Directive. The original EN 50360:2017 and EN 50566:2017 can be used until 1 June 2025.
Click on this link to view the original implementation decision.
This regulation shall enter into force on the date of publication. Click on this link to view the original article (EU) 2023/2444.
On October 4, 2023, the European Commission published Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2023/2392 in the Official Journal of the European Union containing new harmonized standards in support of the Radio Equipment Directive. The "Implementation Decision" has now been implemented, and the key points are updated as follows:
- The cellular equipment standard EN 301 908-1 has been updated to V15.2.1, EN 301 908-1 V15.1.1 will expire on April 4, 2025, and the previous version, EN 301 908-1 V13.1.1, has already expired on September 29, 2023;
- The DAB equipment standard EN 302 077 has been updated to V2.3.1 and EN 302 077-2 V1.1.1 will expire on April 4, 2025.
Click the this link to view the original implementation decision.

According to the bill, smartphones and tablets placed on the EU market must display information about their energy efficiency, battery life, protection against dust and water, and protection against accidental drops. This is the first time that a product on the EU market has been required to display a repairability score.
Ecodesign Act (EU) 2023/1670
In order to improve the energy efficiency and durability of mobile phone and tablet products, strict requirements have been put forward for the maintainability, reliability and recycling of products through eco-design principles such as open repair rights, increased product transparency, and recycling.
According to the requirements of theEcodesign Act, manufacturers, importers or agents are obliged to provide critical spare parts to maintenance personnel within 5-10 working days until 7 years after the end of the sale of the product model on the EU market.
If a battery or back cover assembly is not available to the customer, the manufacturer needs to ensure that the product design meets the following requirements:
1. The cycle life is not less than 500 times, and after 500 times, there is at least 83% of the remaining capacity;
2. The battery cycle life is not less than 1000 times, and after 1000 times, there is at least 80% remaining capacity;
3. The product has IP67 dustproof and waterproof design.
The Act requires manufacturers, importers or agents to publish product repair manuals on their free websites to provide professional technicians or users with information related to the repair and maintenance of products, including product identification, disassembly diagrams, fault diagnosis information, necessary circuit connection diagrams, tag diagrams, and disassembly tool requirements.
In order to improve the durability of mobile phones and tablets, the bill requires that products must meet certain reliability requirements
1. Anti-drop design;
2. Mohs 4 hardness screen design;
3. IP44 dustproof and waterproof design
4. The battery cycle life is not less than 500 times;
5. Improve the battery management function and optimize the charging efficiency
6. Availability of operating system upgrades: at least 5 years after the product is placed on the market;
7. Professional repairers use any software or firmware required for replacement without discrimination.
Energy Efficiency Rating Labelling Act (EU) 2023/1669
According to the Act, all smartphones and tablets must be labelled with an energy efficiency rating and registered on the EU's public goods database EPREL before they can be placed on the market.
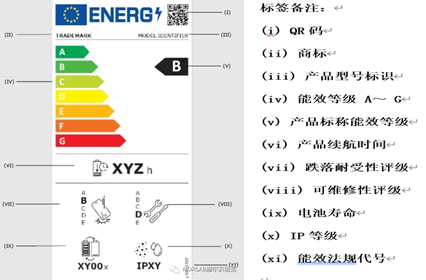
Energy efficiency labels for smartphones and tablets
In response to the two new EU Directives, the CTTL-Terminal Labs can provide a complete evaluation program for enterprises, and can contact xialijiao@caict.ac.cn if necessary.
On July 28, 2023, the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union published a new regulation on batteries and waste batteries, Regulation (EU) 2023/1542. The regulation aims to promote a circular economy in the battery industry by regulating all stages of the battery life cycle, including production, reuse, and recycling. The regulation includes labeling and information requirements for battery components and outlines targets for the recycling of used battery materials, as well as requirements for the carbon footprint of batteries (which does not apply to portable batteries). The regulation was codified on 12 July 2023, published in the Official Journal of the European Union on 28 July 2023, and will enter into force on 18 August 2023
- Chapter 13 of the Regulation, from 18 August 2025, all batteries shall bear a separate recycling mark, from 18 August 2026, the relevant labelling requirements of the Regulation shall be fully implemented, from 18 February 2027 all batteries shall have a QR code containing the battery information required by the Regulations;
- Chapter 11 of the Regulation (Removable and replaceable requirements for portable batteries and LMT batteries): 18 February 2027;
- Directive 2006/66/EC, which replaces this regulation, will be repealed from 18 August 2025.
Click on this link to view the original Regulation (EU) 2023/1542.
